Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy In Iran
Best arthroscopy hospital in Iran
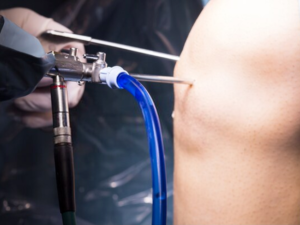 A large number of Iranian and foreign patients are going under arthroscopy in Iran each month. arthroscopy in Iran is on top of the middle-east regarding its skilled specialists and surgeons. Here are the best hospitals for arthroscopy in Iran:
A large number of Iranian and foreign patients are going under arthroscopy in Iran each month. arthroscopy in Iran is on top of the middle-east regarding its skilled specialists and surgeons. Here are the best hospitals for arthroscopy in Iran:
- Treata Professional Hospital
- Gandi Hospital
- Moheb Mehr Hospital
Arthroscopy cost in Iran
There is a significant difference between the cost of arthroscopy in Iran and other countries. The most important factors for the low price of it in Iran are:
- A large number of arthroscopy hospitals in Iran.
- A large number of applicants for arthroscopy in Iran.
Arthroscopy cost in Iran varies depending on the arthroscopy and the hospital. An average cost of arthroscopy in Iran is
Arthroscopy cost in Iran in comparison with other countries
This surgery costs $0 in the U.S., $ in Europe, $ in Thailand and $2300 in Turkey.
Best arthroscopy surgeon in Iran
A lot of orthopaedic surgeries are being performed each year in Iran. Experienced Iranian doctors with an excellent record are performing the operations. One of the most important factors for choosing a good surgeon for arthroscopy in Iran is a doctor has done many arthroscopy surgeries.
You can find the best doctors for arthroscopy in Iran on our website by following their different experiences.
Why should you travel to Iran for an arthroscopy?
Many patients travel to Iran for arthroscopy. One of the reasons for this matter is Iranian specialists and surgeons who have high surgery success rates.
- Low cost of arthroscopy in Iran
- Low cost of accommodation in Iran
- Well experienced doctors
- The high number of arthroscopy in Iran
Arthroscopy centres accordant with today's European standards are performing the highest quality operations in Iran. Another reason for arthroscopy in Iran is its lower cost compared to other countries.
How long should I stay for arthroscopy in Iran?
About Arthroscopy
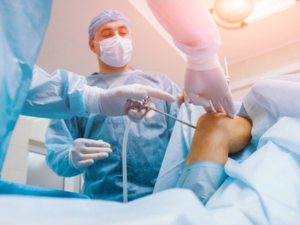 For certain conditions, an arthroscopic repair is better and easier to perform, with less soft-tissue dissection, the minimum time for recovery and much smaller incisions, than performing an “open procedure” surgery to address the problem. Arthroscopic surgery has gone from being an advantage of less invasive surgery to the standard of care for many types of joint surgery. Most commonly performed on the knee and the shoulder, arthroscopic surgery can also be performed on just about any other joint in the body. This type of surgery does not have many complications and patients should not worry if they have a professional orthopaedic team supporting them. Advances in medical technology and arthroscopic techniques have allowed more procedures to be performed arthroscopically.
For certain conditions, an arthroscopic repair is better and easier to perform, with less soft-tissue dissection, the minimum time for recovery and much smaller incisions, than performing an “open procedure” surgery to address the problem. Arthroscopic surgery has gone from being an advantage of less invasive surgery to the standard of care for many types of joint surgery. Most commonly performed on the knee and the shoulder, arthroscopic surgery can also be performed on just about any other joint in the body. This type of surgery does not have many complications and patients should not worry if they have a professional orthopaedic team supporting them. Advances in medical technology and arthroscopic techniques have allowed more procedures to be performed arthroscopically.
Types of Arthroscopy
- Knee Arthroscopy
- Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Hip Arthroscopy
- Ankle Arthroscopy
- Elbow Arthroscopy
- Wrist Arthroscopy Common Arthroscopic Procedures:
- Trimming a torn meniscus of the knee
- Repairing a torn meniscus of the knee
- Treatment of shoulder bursitis
- Repair of the rotator cuff in the shoulder
- Treatment of cartilage damage in the knee
- Treatment of labral tears in the shoulder
Recommended for
The decision should be made by doctor and patient both
Before Arthroscopy
Exact preparations depend on which of the joints the surgeon is examining or repairing. Smoking should be stopped few weeks before and after the surgery. Smoking will slow down the healing process. Patients should stop taking Aspirin, anti-inflammatory medicines and herbal supplements before the surgery since these medicines increase the risk of bleeding. They should not eat or drink after midnight the night before the surgery. Patients should wear loose, comfortable clothing.
During Arthroscopy
When an arthroscopy is performed, a camera is inserted into the joint through a small incision (about one centimetre). The arthroscopic surgery camera is attached to a fiberoptic light source and shows a picture of the inside of the joint on a television monitor. The surgeon uses fluid pumped through the joint to aid in visibility and clear debris from the joint. One or more other incisions are made to insert instruments that can treat a variety of conditions. For example, a shaver can be inserted to trim torn cartilage from a joint.
Recovery
Patients can go home the same day or the day after the procedure. Patients may feel some pain after the procedure. The surgeon may prescribe some painkillers and antibiotics. At home, they may find it helpful to rest, ice, compress and elevate the joint for several days to reduce swelling and pain. They might need to use temporary splints — slings or crutches for comfort and protection. The doctor might prescribe physical therapy and rehabilitation to help strengthen the muscles and improve the function of the joint.
